链表
移除链表元素
LeetCode.203
很基础的链表操作,需要注意删除头节点与删除其他节点操作不同;
核心代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* p = head;
while(p!=nullptr){
if(p->val == val){
if(p==head){
head=p->next;
}else{
slow->next = p->next;
p = p->next;
}
}else{
slow = p;
p=p->next;
}
}
return head;
}
|
设计链表
LeetCode.707
思路很简单,主要考察有没有注意一些细节,核心代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
| struct MyListNode{
int val;
MyListNode* next;
MyListNode():val(0),next(nullptr){}
MyListNode(int v):val(v),next(nullptr){}
};
class MyLinkedList {
public:
MyLinkedList(){
dummyHead = new MyListNode();
ListLength = 0;
}
int get(int index) {
if(index<ListLength){
int i=0;
MyListNode* p = dummyHead->next;
while(i<index){
p=p->next;
i++;
}
return p->val;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
void addAtHead(int val) {
MyListNode* p = new MyListNode(val);
p->next = dummyHead->next;
dummyHead->next = p;
ListLength++;
}
void addAtTail(int val) {
MyListNode* p = dummyHead;
while(p->next!=nullptr){
p=p->next;
}
MyListNode* newNode = new MyListNode(val);
p->next = newNode;
ListLength++;
}
void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if(index<ListLength){
MyListNode* p=dummyHead;
int i=0;
while(i<index){
p=p->next;
i++;
}
MyListNode* newNode = new MyListNode(val);
newNode->next = p->next;
p->next = newNode;
ListLength++;
}else if(index==ListLength){
addAtTail(val);
}
}
void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if(index<ListLength){
MyListNode* p = dummyHead;
int i=0;
while(i<index){
p=p->next;
i++;
}
p->next = p->next->next;
ListLength--;
}
}
private:
MyListNode* dummyHead;
int ListLength = 0;
};
|
反转链表(⭐⭐)
LeetCode.206
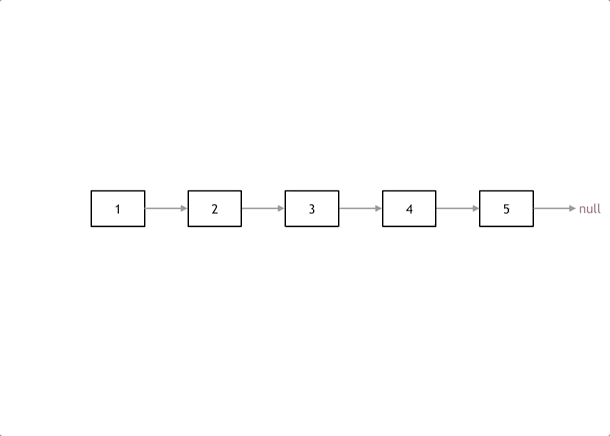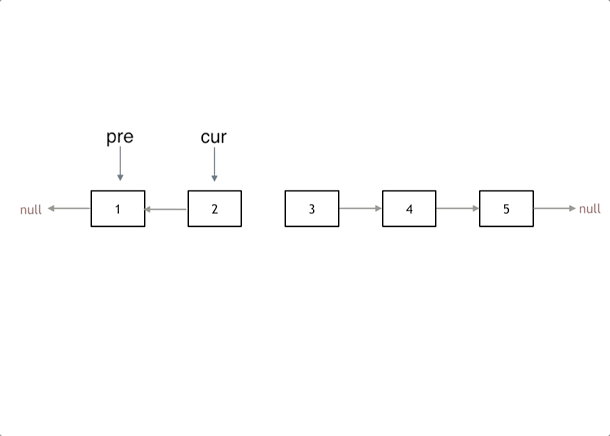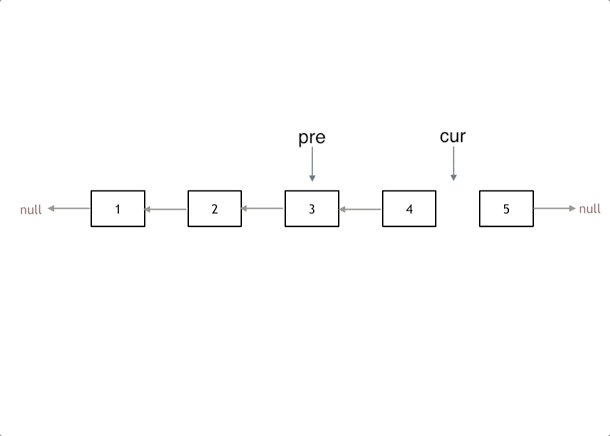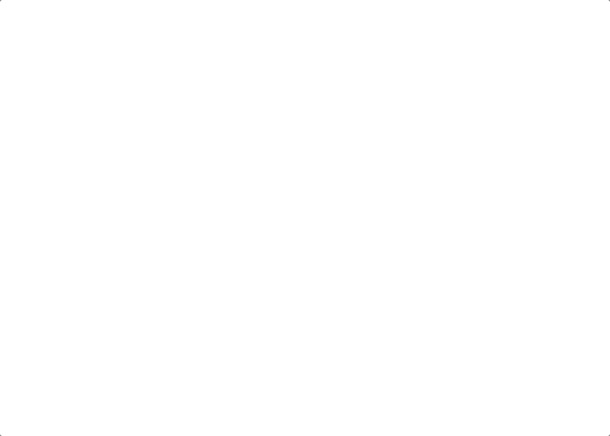
本题有递归法和双指针法两种解法,递归法就是严格按照双指针思路写的;
核心代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur!=nullptr){
ListNode* temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
head = pre;
return head;
}
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* cur, ListNode* pre){
if(cur==nullptr){
return pre;
}
ListNode* temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
return reverse(temp, cur);
}
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head){
return reverse(head, nullptr);
}
|
两两交换链表中的节点(⭐)
LeetCode.24
链表题最好做的时候画图帮助理解:
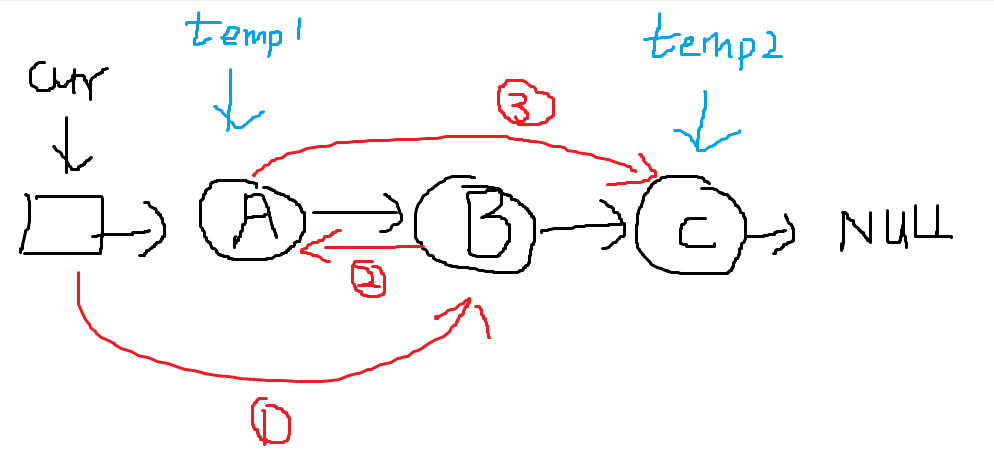
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode* cur = dummyHead;
while(cur->next!=nullptr&&cur->next->next!=nullptr){
ListNode* temp1 = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
ListNode* temp2 = cur->next->next;
cur->next->next = temp1;
temp1->next = temp2;
cur=cur->next->next;
}
return dummyHead->next;
}
|
删除链表的倒数第N个节点
LeetCode.19
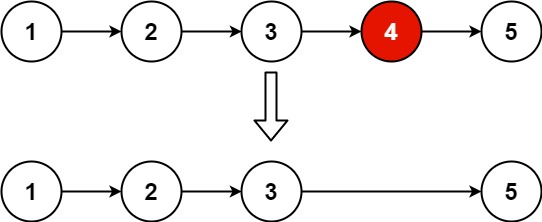
本题是典型的快慢指针,可以实现一次循环删除倒数第N个节点,时间复杂度O(N);
注意:涉及链表删除的题目要使用虚拟头节点! 可以确保删除头结点时操作和删除中间节点相同,不容易写错;
关键代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode* slow = dummyHead;
ListNode* fast = head;
int i=0;
while(i<n){
fast=fast->next;
i++;
}
while(fast!=nullptr){
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next;
}
slow->next=slow->next->next;
return dummyHead->next;
|
相交链表(⭐)
LeetCode.160
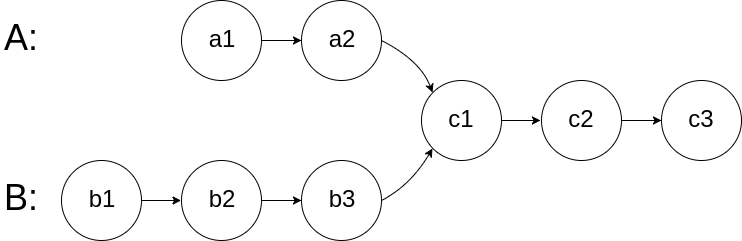
思路为先分别求两个链表长度,之后让长链表移动到与短链表长度相同的位置,再同时向后移动两个链表并比较是否相等;
核心代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
int lenA=0, lenB=0;
ListNode* pA = headA;
ListNode* pB = headB;
while(pA!=nullptr){
pA=pA->next;
lenA++;
}
while(pB!=nullptr){
pB=pB->next;
lenB++;
}
pA=headA;
pB=headB;
if(lenA>lenB){
int diff = lenA-lenB;
while(diff--){
pA=pA->next;
}
}else{
int diff = lenB-lenA;
while(diff--){
pB=pB->next;
}
}
while(pA!=nullptr){
if(pA==pB){
return pA;
}
pA=pA->next;
pB=pB->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
|
环形链表(⭐⭐⭐)
LeetCode.142
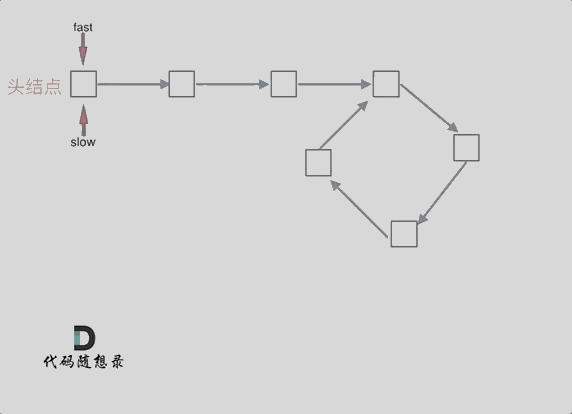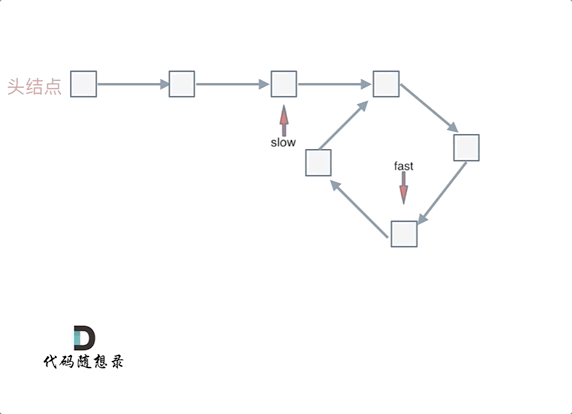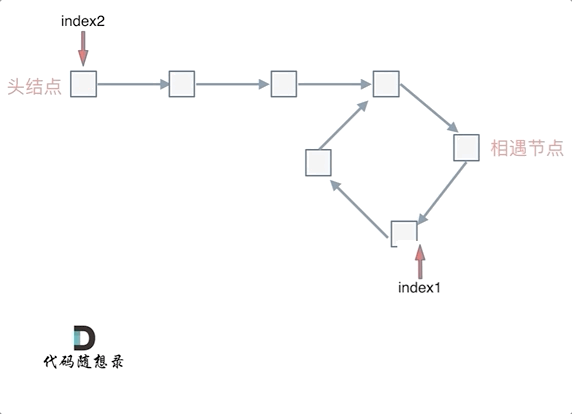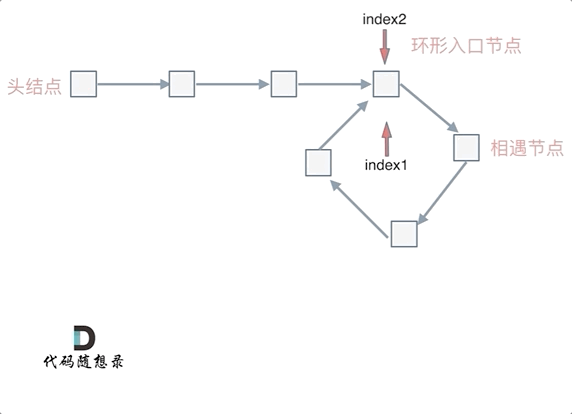
本题有一些技巧,首先是如何判断链表有环,使用快慢指针,快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,如果有环则一定会套圈;之后要判断环的入口在哪:
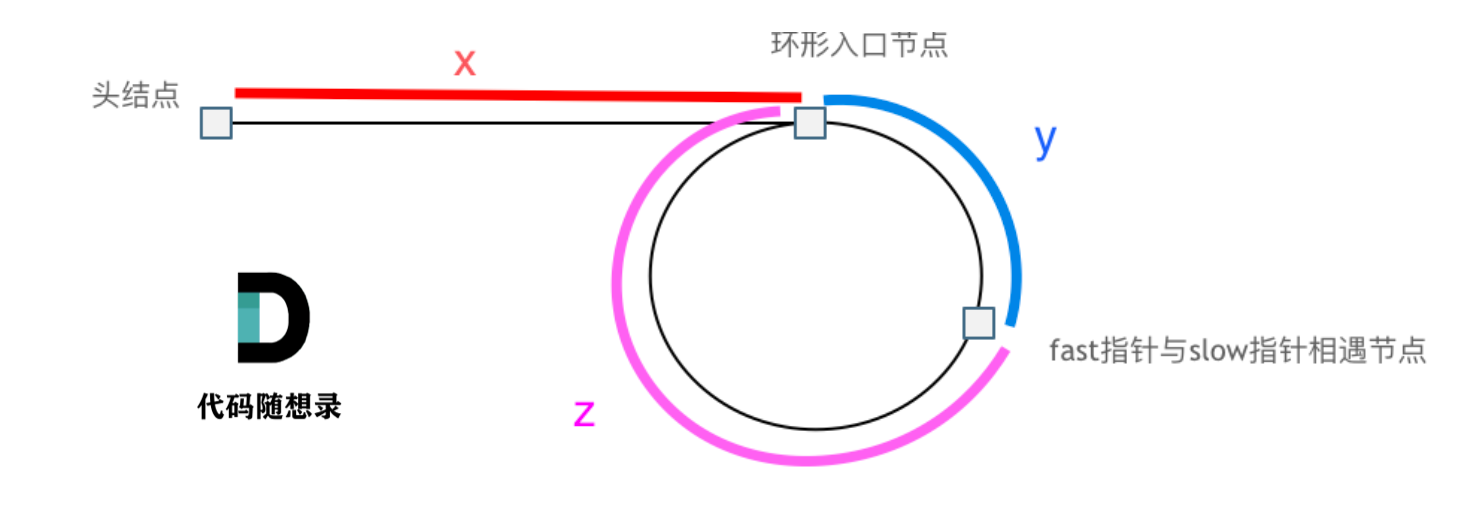
做如上图所示的假设,慢指针走过的路程为(x+y),快指针走过的路程为(x+y+n*(y+z)),且由快指针一次两步,慢指针一次一步可以列出等式 2(x+y)=x+y+n(y+z) ,经过计算可得 x=z,因此可以记录相遇点,从相遇点和头节点同时向后移动即可找到环的入口:
核心代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while(fast!=nullptr&&fast->next!=nullptr){
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
if(fast==slow){
ListNode* index1=slow;
ListNode* index2=head;
while(index1!=index2){
index1=index1->next;
index2=index2->next;
}
return index1;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
|





