二叉树
二叉树的递归遍历(⭐⭐⭐)
写递归函数的思考逻辑:(⭐⭐⭐)
- 确定递归函数的参数和返回值
- 确定终止条件
- 确定单层递归的逻辑
前序遍历:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| void traversal(TreeNode* cur, vector<int>& res){
if(cur==nullptr) return;
res.push_back(cur->val);
traversal(cur->left, res);
traversal(cur->right, res);
}
|
中序遍历:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| void traversal(TreeNode* cur, vector<int>& res){
if(cur==nullptr) return;
traversal(cur->left, res);
res.push_back(cur->val);
traversal(cur->right, res);
}
|
后序遍历:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| void traversal(TreeNode* cur, vector<int>& res){
if(cur==nullptr) return;
traversal(cur->left, res);
traversal(cur->right, res);
res.push_back(cur->val);
}
|
二叉树的迭代遍历(非递归)(⭐⭐⭐)
前序遍历:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
stack<TreeNode*> stack;
if(root==nullptr){
return res;
}
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.empty()){
TreeNode* temp=stack.top();
res.push_back(temp->val);
stack.pop();
if(temp->right!=nullptr){
stack.push(temp->right);
}
if(temp->left!=nullptr){
stack.push(temp->left);
}
}
return res;
}
|
中序遍历:(⭐⭐⭐)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if(root==nullptr){
return res;
}
stack<TreeNode*> stack;
TreeNode* cur=root;
while(cur!=nullptr||!stack.empty()){
if(cur!=nullptr){
stack.push(cur);
cur=cur->left;
}else{
cur = stack.top();
res.push_back(cur->val);
stack.pop();
cur=cur->right;
}
}
return res;
}
|
后序遍历:
后序遍历的非递归算法有些技巧,不需要模拟后序遍历的递归栈;前序遍历顺序是 中左右,后序遍历顺序是 左右中,因此可以使用前序遍历顺序为中右左得到数组,再reverse数组即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if(root==nullptr){
return res;
}
stack<TreeNode*> stack;
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.empty()){
TreeNode* tempNode=stack.top();
stack.pop();
res.push_back(tempNode->val);
if(tempNode->left!=nullptr){
stack.push(tempNode->left);
}
if(tempNode->right!=nullptr){
stack.push(tempNode->right);
}
}
reverse(res.begin(),res.end());
return res;
}
|
二叉树的层序遍历(⭐⭐⭐)
二叉树的层序遍历(⭐⭐)
LeetCode.102
核心代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if(root==nullptr){
return res;
}
queue<TreeNode*> queue;
queue.push(root);
while(!queue.empty()){
int size=queue.size();
vector<int> secVec;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
TreeNode* tempNode=queue.front();
queue.pop();
secVec.push_back(tempNode->val);
if(tempNode->left!=nullptr){
queue.push(tempNode->left);
}
if(tempNode->right!=nullptr){
queue.push(tempNode->right);
}
}
res.push_back(secVec);
}
return res;
}
|
二叉树的层序遍历Ⅱ
LeetCode.107
和上一题一样,最后翻转结果数组即可;
核心代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if(root==nullptr){
return res;
}
queue<TreeNode*> queue;
queue.push(root);
while(!queue.empty()){
int size=queue.size();
vector<int> secVec;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
TreeNode* tempNode=queue.front();
secVec.push_back(tempNode->val);
queue.pop();
if(tempNode->left!=nullptr){
queue.push(tempNode->left);
}
if(tempNode->right!=nullptr){
queue.push(tempNode->right);
}
}
res.push_back(secVec);
}
reverse(res.begin(),res.end());
return res;
}
|
二叉树的右视图
LeetCode.199
核心代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| while(!queue.empt()){
int size=queue.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
if(i==size-1){
res.push_back(tempNode->val);
}
}
}
|
二叉树的层平均值
LeetCode.637
核心代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| while(!queue.empt()){
int size=queue.size();
double sum=0
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
sum+=tempNode->val;
}
res.push_back(sum/size);
}
|
N叉树的层序遍历
LeetCode.429
核心代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| while(!queue.empt()){
int size=queue.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
res.push_back(node->val);
for(int i=0;i<node->children.size();i++){
if(node->children[i]!=nullptr){
queue.push(node->children[i]);
}
}
}
}
|
在每个树行中找最大值
LeetCode.515
记录最大值即可。
翻转二叉树
LeetCode.226
核心代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
void invert(TreeNode* root){
if(root==nullptr) return;
swap(root->right, root->left);
invert(root->left);
invert(root->right);
}
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root){
invert(root);
return root;
}
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr){
return root;
}
stack<TreeNode*> stack;
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.empty()){
TreeNode* node=stack.top();
stack.pop();
swap(node->left, node->right);
if(node->left){
stack.push(node->left);
}
if(node->right){
stack.push(node->right);
}
}
return root;
}
|
对称二叉树(⭐)
LeetCode.101
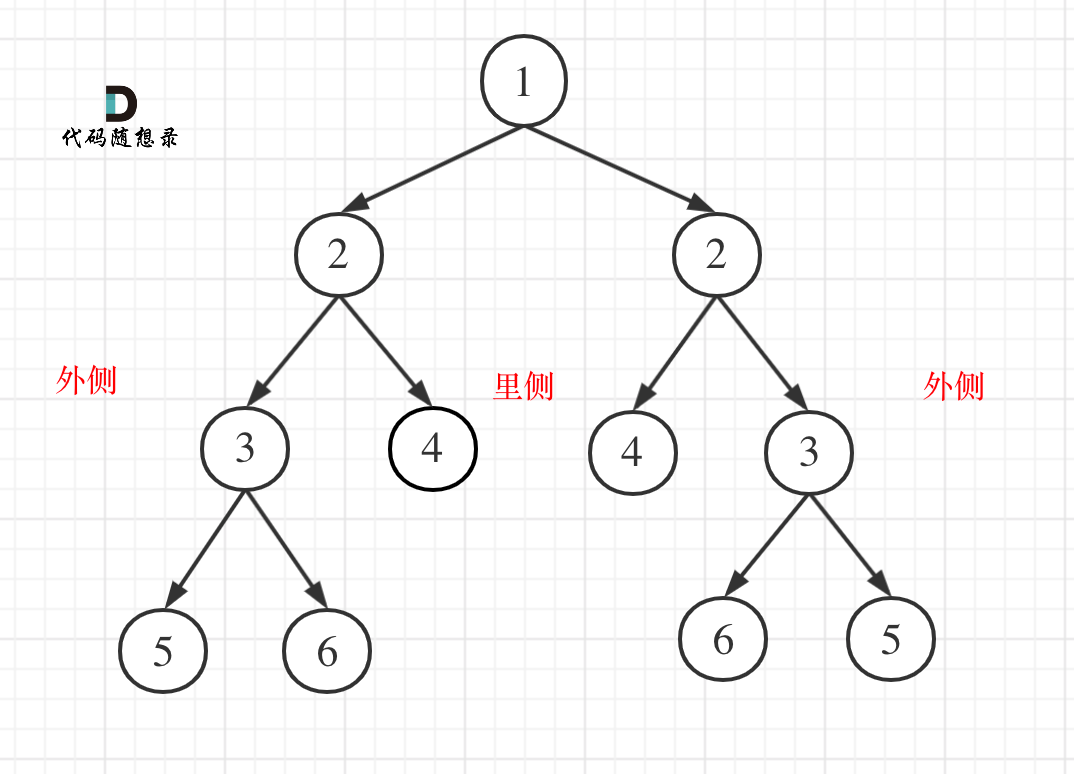
核心代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
bool compare(TreeNode* leftNode, TreeNode* rightNode){
if(!leftNode&&rightNode){
return false;
}else if(leftNode&&!rightNode){
return false;
}else if(!leftNode&&!rightNode){
return true;
}else if(leftNode->val!=rightNode->val){
return false;
}
bool outside=compare(leftNode->left, rightNode->right);
bool inside=compare(leftNode->right, rightNode->left);
return outside&&inside;
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
return compare(root->left, root->right);
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
st.push(root->left);
st.push(root->right);
while(!st.empty()){
TreeNode* rightNode=st.top();
st.pop();
TreeNode* leftNode=st.top();
st.pop();
if(!rightNode&&!leftNode){
continue;
}
if((!rightNode||!leftNode||(rightNode->val!=leftNode->val))){
return false;
}
st.push(leftNode->left);
st.push(rightNode->right);
st.push(leftNode->right);
st.push(rightNode->left);
}
return true;
}
|
二叉树的最大深度
LeetCode.104
核心代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
int func(TreeNode* root){
if(root==nullptr){
return 0;
}
int leftDepth=func(root->left);
int rightDepth=func(root->right);
return max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr){
return 0;
}
return func(root);
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr) return 0;
int res=0;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
int size = que.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
TreeNode* node=que.front();
que.pop();
if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
res+=1;
}
return res;
}
|
二叉树的最小深度(⭐)
LeetCode.111
本题递归法和求二叉树最大深度类似,只是要处理没有子树的情况,如一个树只有右子树,他的最小深度不是1;
本题迭代法使用层序遍历,当一个节点没有左右儿子时说明其是叶子节点,故第一次遇到没有左右儿子的节点时就是最小深度;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr) return 0;
int depth=0;
int leftDepth=minDepth(root->left);
int rightDepth=minDepth(root->right);
if(leftDepth!=0&&rightDepth!=0){
depth = min(leftDepth, rightDepth);
}else if(leftDepth==0){
depth=rightDepth;
}else{
depth=leftDepth;
}
return depth+1;
}
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int depth = 0;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (node->left)
que.push(node->left);
if (node->right)
que.push(node->right);
if (!node->left && !node->right) {
return depth;
}
}
}
return depth;
}
|
完全二叉树的节点个数
本题直接求个数了,没用到完全二叉树的性质;
平衡二叉树(⭐)
LeetCode.110
核心代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| int getHeight(TreeNode* root){
if(root==nullptr){
return 0;
}
int leftHeight=getHeight(root->left);
int rightHeight=getHeight(root->right);
if(leftHeight==-1||rightHeight==-1){
return -1;
}
if(abs(leftHeight-rightHeight)<=1){
return max(leftHeight, rightHeight)+1;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root){
if(root==nullptr) return true;
if(getHeight(root)!=-1){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
|
二叉树的所有路径(⭐)
LeetCode.257
关键在于理解二叉树的遍历;
核心代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root){
vector<string> res;
stack<TreeNode*> treeSt;
stack<string> pathSt;
treeSt.push(root);
pathSt.push(to_string(root));
while(!treeSt.empty()){
TreeNode* node=treeSt.top(); treeSt.pop();
string path=pathSt.top(); pathSt.pop();
if(!node->left&&!node->right){
res.push_back(path);
}
if(node->right){
treeSt.push(node->right);
pathSt.push(path+"->"+to_string(node->right->val));
}
if(node->left){
treeSt.push(node->left);
pathSt.push(path+"->"+to_string(node->left->val));
}
}
return res;
}
|
